North Korea Adds Deepfakes & GenAI to Their Arsenal
Learn how North Korea is utilizing deepfakes and GenAI as part of their arsenal and how AI detection can help spot deepfakes and fake content.

North Korea Adds Deepfakes & GenAI to Their Arsenal
North Korea's economy is predicated on cybercrime. From sophisticated phishing attacks to crypto hacks. Between their various forms of cybercrime, including cryptocurrency theft to ransomware, 8% of their $48.3 billion GDP is made of such activities. When Generative AI became popular, San Francisco wasn't the only place excited about it.
The isolated nation has long been known for its cyber capabilities, but the integration of deepfake technology into their arsenal adds a new technology used for scams.
Metric | Value | ||
Total GDP | $48.3 billion | ||
Cybercrime Contribution to GDP | 8% | ||
Foreign Currency Income from Cyber Attacks | 50% | ||
Amount Stolen (2017-2023) | $3 billion | ||
Number of Crypto Attacks (2017-2023) | 58 |
North Korea's universities are the breeding grounds for its cyber army. At institutions like Pyongyang University of Automation and Mirim College, students don't just learn coding - they master the dark arts of digital warfare.
The curriculum is comprehensive:
Deep dives into operating systems, especially Windows
Malware development and deployment
Cryptocurrency theft techniques
Social engineering and phishing strategies
Artificial Intelligence & neural networks
Students engage in hands-on exercises, simulating real-world attacks. Some even receive advanced training abroad, particularly in China.
The elite cybercrime bootcamps produce about 100 skilled hackers annually. They graduate ready to join elite units like the infamous Lazarus Group, reposible for attacks costing organizations billions.
In cybersecurity, it's always Day 1. In detection of deepfakes and AI, it's Day 0.
North Korea's Cybercrime History
North Korea's cyber arsenal has been a set of tactics that have proven effective and profitable:
Spear-phishing: Crafting personalized emails to trick targets into revealing sensitive information, often impersonating trusted entities like journalists or academics
Malware Development: Creating sophisticated tools like ReconShark for precision attacks, focusing on exploiting vulnerabilities in common operating systems
Cryptocurrency Heists: Infiltrating exchanges and wallets with advanced hacking techniques, ie the $620 million theft from Sky Mavis' Ronin Network
Ransomware Attacks: Encrypting victims' data and demanding payment for its release such as The WannaCry attack of 2017 affected over 200,000 computers worldwide
Social Engineering: Manipulating individuals to divulge confidential information using smishing (SMS phishing)
These methods have yielded significant results. Between 2017 and 2023, North Korean hackers conducted 58 cyberattacks on cryptocurrency-related companies alone, amassing approximately $3 billion.
North Korean Incorporating AI and Deepfakes into Cybercrime Operations
North Korea's cybercrime toolkit has gotten a recent boost, opening up new possibilities for sophisticated attacks and spreading disinformation.
What Are Deepfakes?
Deepfakes are a specific application of generative AI, focusing on the creation or manipulation of audio and visual content. Using deep learning algorithms, deepfakes can superimpose or replace faces, voices, and movements in videos, creating highly convincing deepfake video and images. These systems and models are trained on vast datasets and can produce outputs that closely mimic human-created content, audio and mannerisms. Techniques such as Generative Adversarial Network (GAN) are creating deepfakes and face swaps.
North Korea's Deepfake Investment
North Korea's focus on deepfake technology serves multiple strategic purposes:
Disinformation campaigns - Creating and disseminating false narratives to influence public opinion or political processes
Enhanced social engineering - Developing highly convincing fake identities for more effective scams and infiltration
Extortion and blackmail - Producing seemingly authentic compromising content for leverage
Security system evasion - Circumventing biometric checks, voice recognition, and other AI-based security measures
For North Korea, the use of deepfakes offers a cost-effective method of causing significant disruption and grow their multi-billion cybercrime economy. This technology allows them to conduct sophisticated cyber operations with far-reaching global consequences, all while maintaining plausible deniability.
Real Life Example: A Deepfake Trojan Horse
The recent attack of KnowBe4, a US-based publicly traded cybersecurity training firm, by a North Korean hacker demonstrates the evolving sophistication of their cyber operations. This incident highlights the combination of technical skills and social engineering employed by state-sponsored threat actors.
The hacker's strategy was multi-faceted:
Enhanced Identity Theft: They created a convincing digital persona using a stolen U.S.-based identity, augmented with AI-generated photos.
Recruitment Process Exploitation: The hacker successfully navigated a complex hiring process, including four video interviews and background checks.
Rapid Malware Deployment: Upon receiving the company laptop, they immediately began loading malware, indicating clear objectives and technical expertise.
Remote Work Deception: The use of an "IT mule laptop farm" and VPN routing through North Korea or China created the illusion of a U.S.-based remote worker.
Luckily, KnowBe4's security team flagged this activity before their company was another revenue source for cybercrime.
This incident underscores several critical points:
The integration of traditional hacking methods with advanced identity fraud and AI generated content.
Deepfakes can fool even publicly traded companies in the cybersecurity sector.
The extensive measures North Korean operatives are willing to take to infiltrate high-value targets.
Kudos to KnowBe4 for sharing details, which serves as a reminder that in the realm of cybersecurity, trust must always be verified.
Add AI & Deepfake Detection to Your Security Arsenal
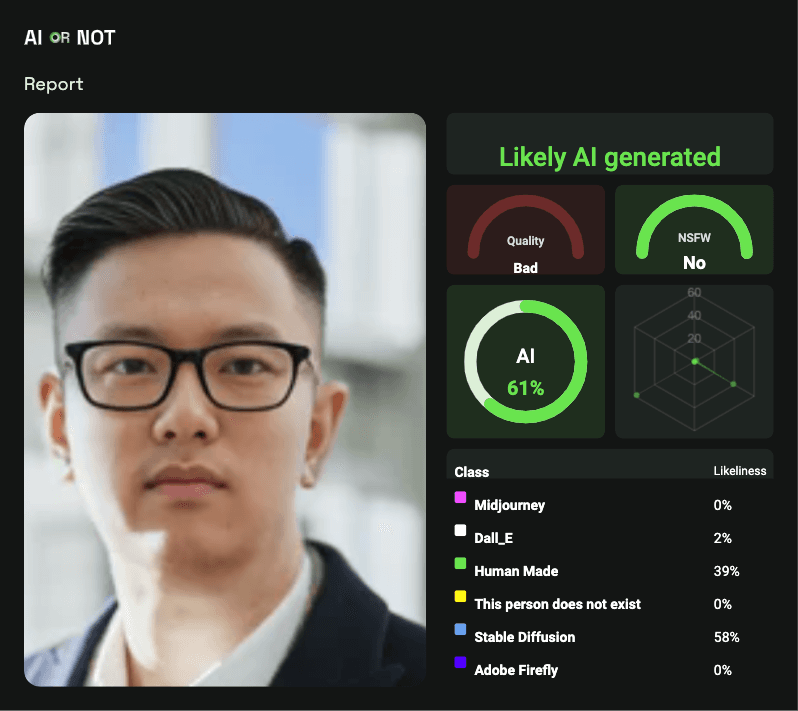
How AI Detection Works
AI detection systems use advanced algorithms to analyze various elements of digital content:
Image Analysis: Scrutinizes pixel-level inconsistencies, unnatural lighting, and facial anomalies.
Audio Examination: Identifies irregularities in voice patterns, background noise, and acoustic properties.
These systems offer protection against various deepfake threats:
KYC Verification: Ensures the authenticity of identity documents and selfies in financial services.
Social Media Monitoring: Identifies and flags deepfake, fake news content before it goes viral.
Phishing: Detects AI-generated phishing attempts.
Staying Ahead
North Korea's adoption of AI and deepfake technology in their cybercrime arsenal adds to an already expansive digital threat landscape. From sophisticated phishing attacks to the infiltration of high-profile targets, these tools have amplified the scope and impact of cybercrime operations.
Just as they have added to their suite of tools, so should we with AI detection. Using AI to fight AI, detection adds the ability to analyze images, audio, and video gives us the ability to stop adversarial misinformation and deceit. Spotting deepfakes is not a task left to humans alone. As threat actors refine their techniques, AI detection systems do too, creating an ongoing cycle of innovation in cybersecurity. Its ability to analyze images, audio, and video provides protection against even the most convincing digital deceptions.